Authors:
(1) Hamid Reza Saeidnia, Department of Information Science and Knowledge Studies, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Islamic Republic of Iran;
(2) Elaheh Hosseini, Department of Information Science and Knowledge Studies, Faculty of Psychology and Educational Sciences, Alzahra University, Tehran, Islamic Republic of Iran;
(3) Shadi Abdoli, Department of Information Science, Université de Montreal, Montreal, Canada
(4) Marcel Ausloos, School of Business, University of Leicester, Leicester, UK and Bucharest University of Economic Studies, Bucharest, Romania.
Table of Links
RQ 4: Future of Scientometrics, Webometrics, and Bibliometrics with AI
RQ 5: Ethical Considerations of Scientometrics, Webometrics, and Bibliometrics with AI
Conclusion, Limitations, and References
Results
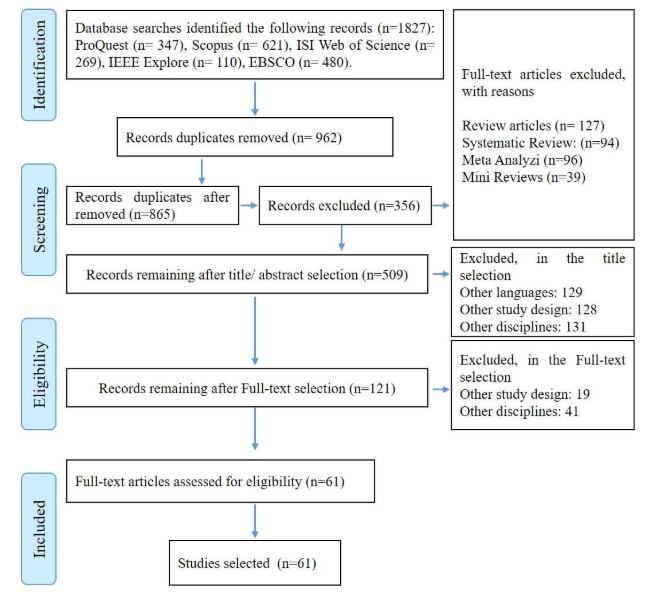
The identification phase of our study involved conducting searches on various databases, such as ProQuest (LISTA & IBSS), EBSCO (LISTA), IEEE Explore, Web of Science, and Scopus. From these databases, a total of 1827 articles were initially found. After removing duplicate articles (962), we were left with 865 articles for further evaluation. By carefully assessing the exclusion criteria based on specific criteria, we excluded 356 articles, resulting in 509 articles for a more thorough analysis of their titles and abstracts. From a full-text analysis, we identified 61 of 121 articles that were relevant to our study's focus on AI in Scientometrics, Webometrics, and Bibliometrics. Therefore, our final dataset consisted of 61 articles, as shown in the flow chart provided in Figure 1.
This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.

